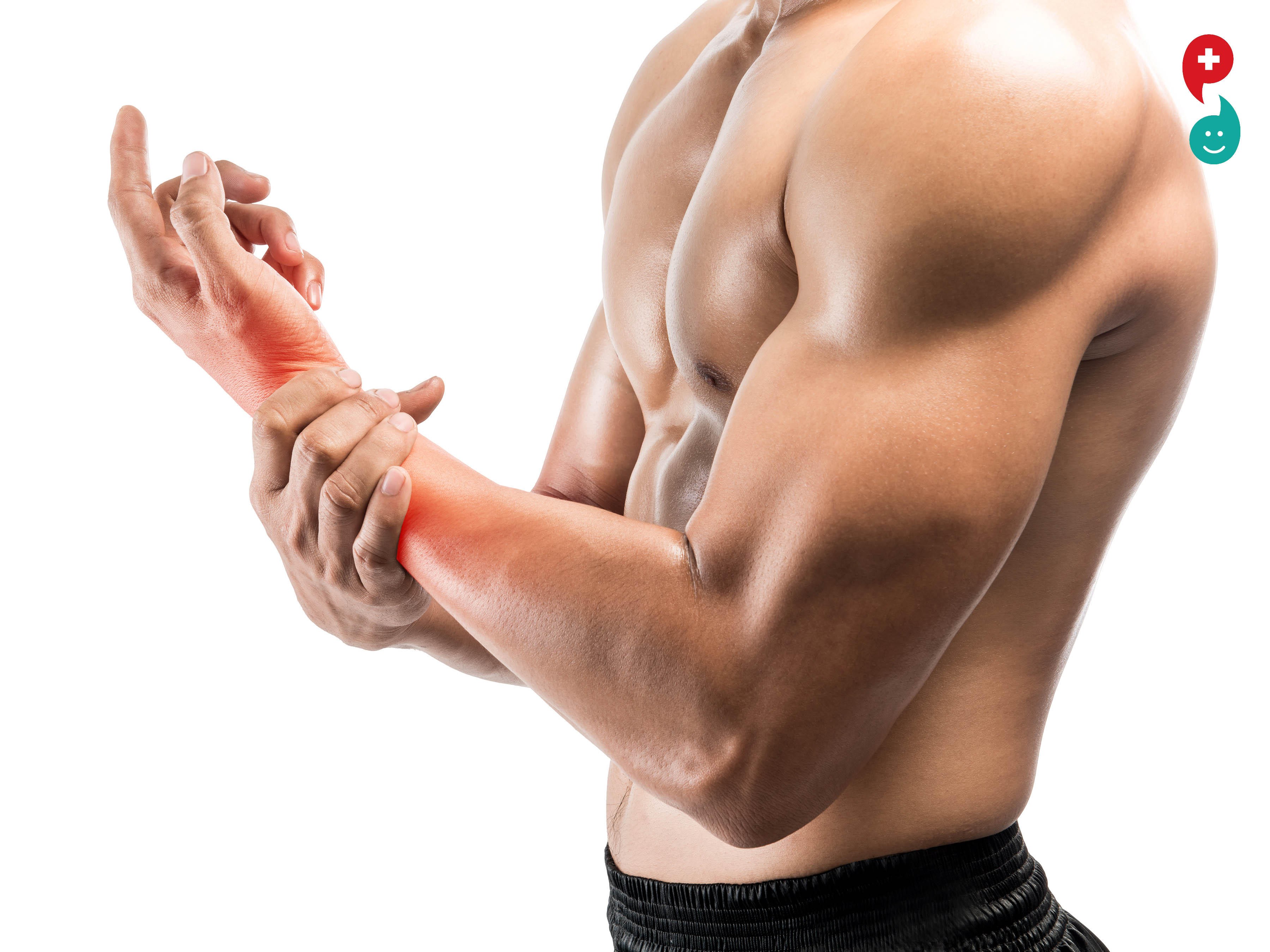
Muscle Strain
What Is It?
Published: December, 2018
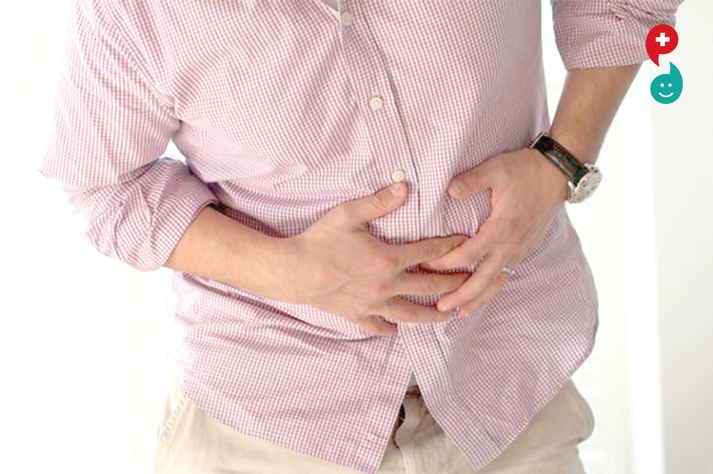
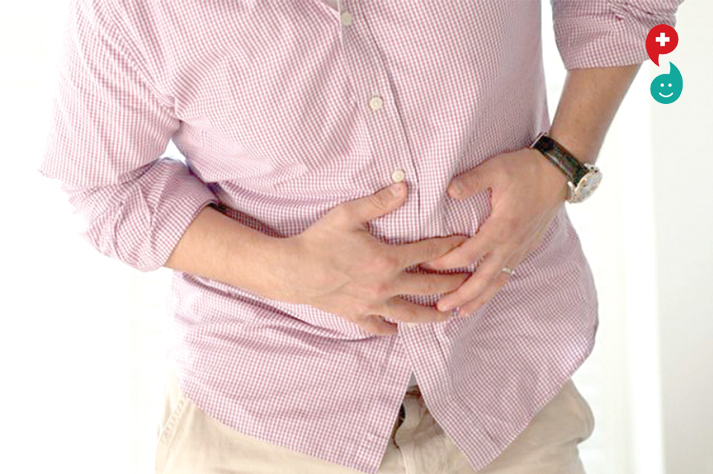
A muscle strain is the stretching or tearing of muscle fibers. Most muscle strains happen for one of two reasons: either the muscle has been stretched beyond its limits or it has been forced to contract too strongly. In mild cases, only a few muscle fibers are stretched or torn, and the muscle remains intact and strong. In severe cases, however, the strained muscle may be torn and unable to function properly. To help simplify diagnosis and treatment, doctors often classify muscle strains into three grades, depending on the severity of muscle fiber damage:
Grade I strain. In this mild strain, only a few muscle fibers are stretched or torn. Although the injured muscle is tender and painful, it has normal strength.
Grade II strain. This is a moderate strain, with a greater number of injured fibers and more severe muscle pain and tenderness. There is also mild swelling, noticeable loss of strength and sometimes a bruise.
Grade III strain. This strain tears the muscle all the way through, sometimes causing a "pop" sensation as the muscle rips into two separate pieces or shears away from its tendon. Grade III strains are serious injuries that cause complete loss of muscle function, as well as considerable pain, swelling, tenderness and discoloration. Because Grade III strains usually cause a sharp break in the normal outline of the muscle, there may be an obvious "dent" or "gap" under the skin where the ripped pieces of muscle have come apart.
Although the risk of muscle strain is especially high during sports activities, you also can strain a muscle by lifting a heavy carton or by simply stepping off a curb.
Almost all types of athletic activity carry some risk of muscle strains, but these injuries tend to happen most often in contact sports, such as football, and in sports that require quick starts, such as basketball and tennis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of muscle strain include:
Muscle pain and tenderness, especially after an activity that stretches or violently contracts the muscle -- Pain usually increases when you move the muscle but is relieved by rest.
Muscle swelling, discoloration or both
Muscle cramp or spasm
Either a decrease in muscle strength or (in Grade III strains) a complete loss of muscle function
A pop in the muscle at the time of injury
A gap, dent or other defect in the normal outline of the muscle (in Grade III strain)
Diagnosis
Your doctor will want to know what type of activity triggered your muscle pain and whether there was a pop in the muscle at the time of injury. The doctor will ask about your symptoms, especially any decrease in muscle strength or any difficulty moving.
Your doctor will want to know whether you've had recent fever, weight loss, leg numbness, urinary or bladder problems, or other symptoms that may point to a more severe medical problem.
After noting your symptoms and past medical history, your doctor will examine you, checking for muscle tenderness, spasm, weakness and decreased muscle movement. If this exam points to a mild or moderate muscle strain, you may not need any additional testing. However, if the diagnosis is in doubt, X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be helpful.
If you have back pain, your doctor may order additional tests to check for a urinary tract infection or a problem involving the vertebrae (backbones), vertebral disks, spinal canal or spinal cord.
Expected Duration
How long a sprain lasts depends on the location and severity of the injury. Symptoms of a mild back strain usually improve within one to two weeks and are gone within four to six weeks. In the legs, mild or moderate strains may take up to 8 to 10 weeks or more to heal. Symptoms of a severe (Grade III) strain may persist until the torn muscle is repaired surgically.
Prevention
To help prevent muscle strains:
Warm up before participating in sports and activities.
Follow an exercise program aimed at stretching and strengthening your muscles.
Increase the intensity of your training program gradually. Never push yourself too hard, too soon.
Maintain a healthy body weight. Obesity can stress muscles, especially in your legs and back.
Practice good posture when you sit and stand.
Use the correct technique when you lift heavy loads.
Treatment
If you have a Grade I or Grade II strain, your doctor will ask you to follow the RICE rule:
Rest the injured muscle (and take a temporary break from sports activities).
Ice the injured area to reduce swelling.
Compress the muscle with an elastic bandage.
Elevate the injured area.
To help relieve muscle pain and swelling, your doctor may suggest that you take acetaminophen (Tylenol and others) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin and others). For someone with a painful back strain that does not improve with NSAIDs or acetaminophen (Tylenol), prescription pain medications or muscle relaxants may be appropriate.
If you have a severe Grade II or Grade III strain, your doctor may refer you to an orthopedic specialist. Depending on the severity and location of your muscle strain, the orthopedist may immobilize the injured muscle in a cast for several weeks or repair it surgically.
Mild strains may heal quickly on their own, but more severe strains may require a rehabilitation program.
When To Call a Professional
Call your doctor promptly if:
You hear or feel a pop in your muscle at the time of injury.
You have severe pain, swelling or discoloration in the injured muscle.
Your injured muscle is obviously weak or has difficulty moving compared to the same muscle on the opposite side of your body.
You have mild muscle symptoms that do not improve after 48 hours.
You have severe back pain that makes it impossible for you to do normal daily activities, or you have mild back pain that worsens after a few days.
You are being treated for a strained back and your symptoms do not improve within two weeks.
You have back pain together with any of the following symptoms, which can signal a medical problem that is more serious than a mild back strain:
Fever or chills
Pain or a burning feeling when you urinate
Sudden weakness, numbness or tingling in a leg
Numbness in your groin or rectum
Difficulty controlling your bladder or bowel function
What is a muscle spasm?
Otherwise known as muscle cramps, spasms occur when a muscle involuntary and forcibly contracts and cannot relax. These are very common and can affect any muscle. Typically, they involve part or all of a muscle, or several muscles in a group. The most common sites for muscle spasms are the thighs, calves, foot arches, hands, arms, abdomen and sometimes along the ribcage. When occurring in the calves, especially, such cramps are known as “charley horses.”
What does a muscle spasm feel like?
Muscle spasms range in intensity from mild twitches to severe pain. The spastic muscle may feel harder than normal to the touch, and/or appear visibly distorted. It may show visible signs of twitching. Spasms may typically last from seconds to 15 minutes or longer, and may recur multiple times before going away.
Who gets muscle spasms?
Muscle spasms can occur at any time to anyone. Whether you are old, young, sedentary or active, you may develop a muscle spasm. It can happen when you walk, sit, perform any exercise, or even sleep. Some individuals are prone to muscle spasms and get them regularly with any physical exertion. However, those who are at greater risk for muscle spasms are infants, the elderly (over age 65), people who overexert during exercise, those who are ill, and endurance athletes.
What causes muscle spasms?
Insufficient stretching before physical activity.
Muscle fatigue.
Exercising in heated temperatures.
Dehydration.
Electrolyte imbalances in potassium, magnesium and calcium.
Muscle pain, also called myalgia, is experienced by many. The most common cause of localized muscle pain is overuse or injury of a muscle (strain). On the other hand, viral infections like influenza (the "flu") may cause systemic muscle pain, as can taking certain medications or having a disease like fibromyalgia or hypothyroidism.
Muscle pain can feel different—aching, cramping, stabbing, or burning—depending on what's behind it. In the end, diagnosing the reason for your muscle pain requires a medical history, physical examination, and sometimes, blood and/or imaging tests. Rarely, a muscle biopsy is required.
Once diagnosed, your doctor will devise a treatment plan—one that will hopefully give you the relief you deserve.
What are muscle aches?
Muscle aches, or myalgia, are extremely common. Almost everybody has experienced discomfort in their muscles at some point.
Because there is muscle tissue in nearly all parts of the body, this type of pain can be felt practically anywhere...
What are the most common causes of muscle aches?
Often, people who experience muscle aches can easily pinpoint the cause. This is because most instances of myalgia result from too much stress, tension, or physical activity. Some common causes include:
muscle tension in one or more areas of the body
overusing the muscle during physical activity
injuring the muscle while engaging in physically demanding work or exercise
What types of medical conditions can cause muscle pain?
Not all muscle aches are related to stress, tension, and physical activity. Some medical explanations for myalgia include:
fibromyalgia
infections, such as the flu, polio, or bacterial infections
autoimmune disorders such as lupus, dermatomyositis, and polymyositis
use of certain medications or drugs, such as statins, ACE inhibitors, or cocaine
thyroid problems, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
hypokalemia (low potassium)
Easing muscle aches at home
Muscle aches often respond well to home treatment. Some measures you can take to relieve muscle discomfort from injuries and overuse include:
resting the area of the body where you are experiencing aches and pains
taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen (Advil)
applying ice to the affected area to help relieve pain and reduce inflammation
Shop for ibuprofen.
You should use ice for one to three days following a strain or sprain, and apply heat for any pain that remains after three days.
Find ice packs and heat packs on Amazon.
Other measures that may provide relief from muscle pain include:
gently stretching the muscles
avoiding high-impact activities until after the muscle pain goes away
avoiding weight-lifting sessions until the muscle pain is resolved
giving yourself time to rest
doing stress-relieving activities and exercises such as yoga and meditation to relieve tension
Pain in back, joints or in muscle can be very troublesome. And if it continues, then it can cause a lot of discomfiture as you then find it difficult to perform even day-to-day activities. Homeopathy very effectively deals with any pain. Let us check the remedies:
Homeopathic remedies for back pain:
1. Arnica: Injured back often leads to severe back pain and it can be well treated by this homeopathic medicine. Both recent and past back-injuries can be treated using this medicine. This medicine is absolutely safe and thus you will not face any side-effects at all. Unwanted back stiffness and soreness within back muscles can also be minimized to a great extent with the consistent application of this medicine. Back motions can be made much more flexible by curtailing restlessness.
2. Bryonia: There are some prominent symptoms of back pain and they can be easily and efficiently alleviated by this medicine. If you have become pretty tired of applying homemade therapies, then you can try out this solution. This medicine can reduce your pain and inflammation within a few hours, and you can get back to your daily activities with great energy. Apart from taking this medicine, you have to take enough rest so that your back can get relaxed. Your back motion can be smoothened and made flexible by taking the concerned medicine.
Ways in which homeopathy can cure Joint and muscle pain:
1. Moving and shifting joint or muscle pains: Many patients have this problem where they face joint or muscle pain but instead of it being constant in one area, it moves around the body. Pulsatilla is known to effectively reduce the symptoms in these cases.
2. Arthritis: One of the most common problems that many people report is that of arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, which causes a lot of pain in many people. In many cases, the use of Natrum Muriaticum and Bryonia has been known to allay the pain.
3. Tennis elbow or tendon related problems: This is a common ailment, which in many cases is caused by strenuous activities, such as sports. Rhus tox has been known to be effective in such cases.
अंग दुखायला लागलं, की अनेकांना ताप आल्यासारखं वाटतं; परंतु अंगदुखीसाठी तापाव्यतिरिक्त अन्यही अनेक कारणं असू शकतात. काहीवेळा या अंगदुखीकडे दुर्लक्ष करणं धोकादायक ठरतं. अचानक एखादी जड वस्तू उचलली गेल्यास किंवा शरीरावर अतिताण पडल्यास अंगदुखी होऊ शकते; परंतु या दोन्ही गोष्टी न करता अंगदुखीचा त्रास सुरू झाल्यास त्याकडे दुर्लक्ष करू नका.
सांधेदुखी : या आजारात सांधे, डोकं आणि हाडं दुखायला लागतात.
तणाव : सततच्या तणावामुळेही डोकेदुखीचा त्रास होतो. झोपेची कमतरता, थकवा, स्नायू किंवा छाती दुखणं इत्यादी कारणांमुळे शरीरावर ताण पडतो आणि त्यातून अंगदुखीचा त्रास सुरू होतो.
टीबी : ट्युबरक्युलेसिस अर्थात क्षयरोग हा तसा फुप्फुसाचा विकार आहे; परंतु टीबीमुळे अनेकदा शरीराच्या इतर भागांतही वेदना होतात.
कॅन्सर : सातत्यानं अतितीव्र स्वरूपातील दुखणं असल्यास ते कॅन्सरचंही लक्षण असू शकतं. कॅन्सरच्या पेशी शरीराच्या इतर भागांत पसरतात आणि त्यातून वेदना वाढतात.
गाठ : शरीराच्या एखाद्या भागात गाठ असेल, तर प्रतिकारशक्तीवर परिणाम होतो. त्यामुळे शरीरातील टीश्यूंवर सूज येते. हे टीश्यू दुखावल्या गेल्यामुळे शरीरात वेदना होतात.
डेंग्यू : डेंग्यूच्या तापामुळेही अंगदुखी वाढू शकते. डेंग्यूच्या तापात अंगदुखीबरोबरच डोकदुखीचाही त्रास होतो.
अधिक व्यायाम : आवश्यकतेपेक्षा अधिक व्यायाम केल्यासही स्नायू आणि सांध्यांमध्ये वेदना होतात. त्यामुळे आपल्या शरीराला मानवेल तितकाच व्यायाम केला पाहिजे.
पोटॅशियमची कमतरता : या आजाराला हायपोकॅलीमिया ही म्हणतात. यात रक्तामधील पोटॅशियमचं प्रमाण कमी होतं. परिणामी, शरीराच्या विविध भागांत दुखायला लागतं.
स्नायू आखडण्यावर उपाय
आपण विविध प्रकारची कामे करतो तेव्हा त्यातल्या कोणत्या तरी कामामुळे आपल्या स्नायूवर मर्यादेपेक्षा अधिक भार पडतो आणि परिणामी तो स्नायू दुखावला तरी जातो किंवा आखडतो. विशेषत: शरीराला न मानवणारा व्यायाम करणे, मर्यादेपेक्षा अधिक वजन उचलण्याचा प्रयत्न करणे, मॅराथॉन स्पर्धेत भाग घेणे किंवा पर्वतावर चढण्याचा प्रयत्न करणे यातून स्नायूवर भार पडतो. अशावेळी खालील प्रकारचे उपाय योजावेत. म्हणजे औषधे न घेताच स्नायूंचे दुखणे कमी होऊ शकते.
स्नायू दुखत असतील तर आपल्या घराच्या आसपास किंवा एखाद्या मोकळ्या मैदानावर फेऱ्या मारा . स्नायू दुखावल्यामुळे आराम करावासा वाटतो, पण तसा आराम टाळून थोडेसे तरी फेऱ्या माराआवश्यक आहे. त्यामुळे रक्तप्रवाह वेगाने सुरू होतो आणि दुखणार्या स्नायूचे दुखणे थांबते. स्नायूच्या दुखण्यावर दुसरा उपाय म्हणजे मालिश करणे. योग्य पद्धतीने आणि योग्य दिशेने मसाज केला म्हणजे स्नायूचे दुखणे कमी होते. मसाज केल्याने रक्तप्रवाह तर सुधारतोच परंतु आखडलेले स्नायू सरळ होतात.
आपल्या शरीरामध्ये खाल्लेल्या अन्नाचे ग्लुकोजमध्ये रुपांतर होते आणि ही ग्लुकोज नावाची शर्करा शरीराला ऊर्जा प्रदान करते. परंतु ग्लुकोज तयार करण्याच्या प्रक्रियेत काही वेळा बाधा येते किंवा पुरेसे ग्लुकोज तयार होत नाही. त्यामुळे स्नायू दुखायला लागल्यावर तर प्रथिनयुक्त अन्नपदार्थ खावेत. त्यामध्ये मांस, मासे, दूध आणि शेंगादाण्यासारखे द्विदल अन्न पदार्थ असावेत. स्नायूच्या आखडण्यावर एक चांगला उपाय म्हणजे दुखावलेल्या स्नायूंना थोडासा ताण देणे.
एक सोपा उपाय म्हणजे भरपूर पाणी पिणे. व्यायाम करण्याच्या आधी, व्यायामाच्या मध्ये आणि व्यायामानंतर भरपूर पाणी पिले पाहिजे. कारण व्यायामाने आपल्या शरीरातील घाम बाहेर पडतो आणि शरीरात पाण्याची कमतरता निर्माण होऊन या कमतरतेचा स्नायूवर परिणाम होऊ शकतो. तेव्हा पाणी पिण्यासारखा साधा उपाय करावा. मात्र तहान लागली म्हणून कॉङ्गी आणि अल्कोहोल यांचा वापर करणे कटाक्षाने टाळावे.