What is Candidiasis?
There are many kinds of fungus that live in the human body. One type is called candida. It’s a type of yeast that normally lives in small amounts in places like your mouth and belly, or on your skin without causing any problems. But when the environment is right, the yeast can multiply and grow out of control.
The infection it causes is called candidiasis. There are several different types of it. Most can be easily treated with over-the-counter or prescription medications.
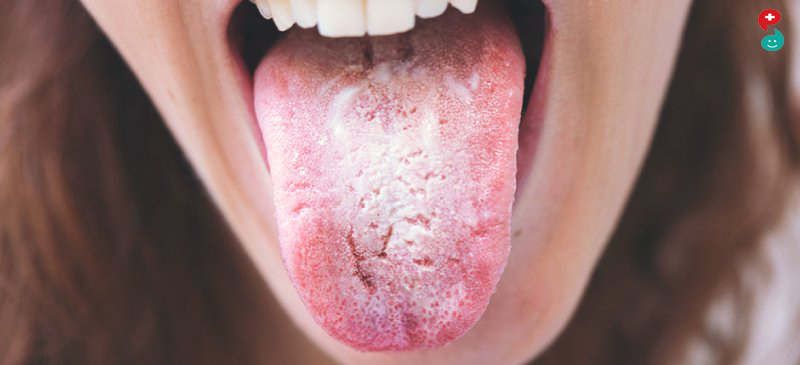
Thrush (Oropharyngeal Candidiasis)
When the candida yeast spreads in the mouth and throat, it can cause an infection called thrush. It’s most common in newborns, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems. Also more likely to get it are adults who:
Are being treated for cancer
Take medications like corticosteroids and wide-spectrum antibiotics
Wear dentures
Have diabetes
The symptoms include:
White or yellow patches on the tongue, lips, gums, roof of mouth, and inner cheeks
Redness or soreness in the mouth and throat
Cracking at the corners of the mouth
Pain when swallowing, if it spreads to the throat
Thrush is treated with antifungal medicines like nystatin, clotrimazole, and fluconazole. Rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine (CHX) mouthwash may help prevent infections in people with weakened immune systems.
Genital Yeast Infection (Genital Candidiasis)
Three out of four adult women will get at least one yeast infection during their lifetime. This occurs when too much yeast grows in the vagina. (Men also can get a genital yeast infection, but it's much less common).
A yeast infection typically happens when the balance in the vagina changes. This can be caused by pregnancy, diabetes, use of some medicines, lubricants, or spermicides, or a weakened immune system. Occasionally, the infection can be passed from person to person during sex.
The symptoms include:
Extreme itchiness in the vagina
Redness and swelling of the vagina and vulva (the outer part of the female genitals)
Pain and burning when you pee
Discomfort during sex
A thick, white “cottage cheese” discharge from the vagina
A man with a yeast infection may have an itchy rash on his penis.
Because the symptoms in women can be similar to other infections like bacterial vaginosis (bacterial overgrowth in the vagina) and sexually transmitted diseases, it’s important to visit your doctor.
Most times, an over-the-counter antifungal suppository, tablet, or cream will knock out the infection. Your doctor might also prescribe a single dose of a prescription antifungal medicine like fluconazole. Tell your doctor if you get yeast infections more than four times a year. She may recommend regular doses of antifungal medication over several months to fight the repeated infections.
Diaper Rash From Yeast Infection
Though diaper rashes are usually caused by leaving a wet or soiled diaper on too long, once your baby’s skin is irritated, infection is more likely. If his diaper rash isn’t going away, check to see if his bottom is red and sensitive, and if there’s a raised red border around the sores. If so, have your pediatrician check for candidiasis. It can be treated with an antifungal cream.
Keeping your baby’s bottom clean and dry is a good start to help prevent diaper rash and candidiasis.
Invasive Candidiasis
If candida yeast enters the bloodstream (usually through medical equipment or devices), it can travel to the heart, brain, blood, eyes, and bones. This can cause a serious, life-threatening infection.
This happens most often to people who have recently been admitted to a hospital or live in a health care facility, such as a nursing home. Like other types of yeast infections, if you have diabetes, a weakened immune system, kidney failure, or are on antibiotics, your chances of getting it are greater.
The symptoms include fever and chills. Since it's likely a person with this infection is already sick with another condition, it can be hard to diagnose.
Invasive candidiasis is treated with an oral or intravenous dose of antifungal medication. If you are having surgery and have higher odds of a yeast infection, your doctor might prescribe a series of antifungal medicines before the procedure.







