Kidney Stone test
What is a kidney stone test?
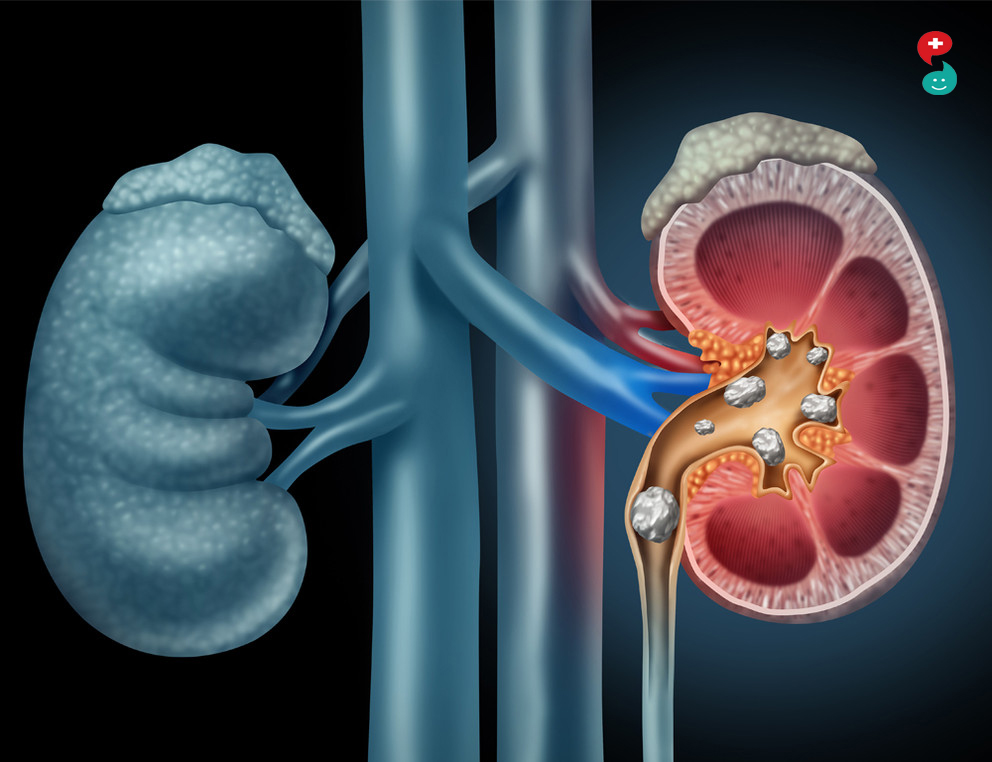
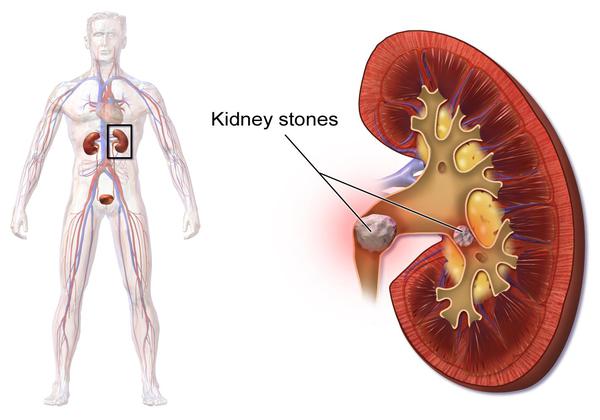
Kidney stones are small, pebble-like substances made from chemicals in your urine. They are formed in the kidneys when high levels of certain substances, such as minerals or salts, get into the urine. A kidney stone analysis is a test that figures out what a kidney stone is made of. There are four main types of kidney stones:
-Calcium, the most common type of kidney stone
-Uric acid, another common type of kidney stone
-Struvite, a less common stone that is caused by urinary tract infections
-Cystine, a rare type of stone that tends to run in families
Kidney stones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Many stones pass through your body when you urinate. Larger or odd-shaped stones can get stuck inside the urinary tract and may need treatment. While kidney stones rarely cause serious damage, they can be very painful.
If you've had a kidney stone in the past, you are likely to get another one. A kidney stone analysis provides information on what a stone is made of. This can help your health care provider develop a treatment plan to reduce your risk of forming more stones.
Other names: urinary stone analysis, renal calculus analysis
What is it used for?
A kidney stone analysis is used to:
-Figure out the chemical makeup of a kidney stone
-Help guide a treatment plan to prevent more stones from forming
Why do I need a kidney stone analysis?
-You may need a kidney stone analysis if you have symptoms of a kidney stone. These include:
-Sharp pains in your abdomen, side, or groin
-Back pain
-Blood in your urine
-Frequent urge to urinate
-Pain when urinating
-Cloudy or bad-smelling urine
-Nausea and vomiting
If you've already passed a kidney stone and you kept it, your health care provider may ask you to bring it in for testing. He or she will give you instructions on how to clean and package the stone.
What happens during a kidney stone analysis?
You will get a kidney stone strainer from your health care provider or from a drug store. A kidney stone strainer is a device made of fine mesh or gauze. It is used to filter your urine. You will also get or be asked to provide a clean container to hold your stone. To collect your stone for testing, do the following:
-Filter all your urine through the strainer.
-After each time you urinate, check the strainer carefully for particles. Remember that a kidney stone -can be very small. It may look like a grain of sand or a tiny piece of gravel.
-If you find a stone, put it in the clean container, and let it dry.
-DO NOT add any fluid, including urine, to the container.
-DO NOT add tape or tissue to the stone.
-Return the container to your health care provider or laboratory as instructed.
If your kidney stone is too large to pass, you may need a minor surgical procedure to remove the stone for testing.
Will I need to do anything to prepare for the test?
You don't need any special preparations for a kidney stone analysis.
Are there any risks to the test?
There is no known risk to having a kidney stone analysis.
What do the results mean?
Your results will show what your kidney stone is made of. Once your health care provider has these results, he or she can recommend steps and/or medicines that may prevent you from forming more stones. The recommendations will depend on the chemical makeup of your stone.
If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
Is there anything else I need to know about a kidney stone test?
It's important to filter all your urine through the kidney stone strainer until you find your kidney stone. The stone may pass at any time, day or night.
Overview
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys.
Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together.
Passing kidney stones can be quite painful, but the stones usually cause no permanent damage if they're recognized in a timely fashion. Depending on your situation, you may need nothing more than to take pain medication and drink lots of water to pass a kidney stone. In other instances — for example, if stones become lodged in the urinary tract, are associated with a urinary infection or cause complications — surgery may be needed.
Your doctor may recommend preventive treatment to reduce your risk of recurrent kidney stones if you're at increased risk of developing them again.
Kidney stone care at Mayo Clinic
Symptoms
A kidney stone may not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureter — the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. At that point, you may experience these signs and symptoms:
Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs
Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin
Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity
Pain on urination
Pink, red or brown urine
Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Nausea and vomiting
Persistent need to urinate
Urinating more often than usual
Fever and chills if an infection is present
Urinating small amounts
Pain caused by a kidney stone may change — for instance, shifting to a different location or increasing in intensity — as the stone moves through your urinary tract.
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs and symptoms that worry you.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Pain so severe that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position
Pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting
Pain accompanied by fever and chills
Blood in your urine
Difficulty passing urine
Causes
Kidney stones often have no definite, single cause, although several factors may increase your risk.
Kidney stones form when your urine contains more crystal-forming substances — such as calcium, oxalate and uric acid — than the fluid in your urine can dilute. At the same time, your urine may lack substances that prevent crystals from sticking together, creating an ideal environment for kidney stones to form.
Types of kidney stones
Knowing the type of kidney stone helps determine the cause and may give clues on how to reduce your risk of getting more kidney stones. If possible, try to save your kidney stone if you pass one so that you can bring it to your doctor for analysis.
Types of kidney stones include:
Calcium stones. Most kidney stones are calcium stones, usually in the form of calcium oxalate. Oxalate is a naturally occurring substance found in food and is also made daily by your liver. Some fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and chocolate, have high oxalate content.
Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, intestinal bypass surgery and several metabolic disorders can increase the concentration of calcium or oxalate in urine.
Calcium stones may also occur in the form of calcium phosphate. This type of stone is more common in metabolic conditions, such as renal tubular acidosis. It may also be associated with certain migraine headaches or with taking certain seizure medications, such as topiramate (Topamax).
Struvite stones. Struvite stones form in response to an infection, such as a urinary tract infection. These stones can grow quickly and become quite large, sometimes with few symptoms or little warning.
Uric acid stones. Uric acid stones can form in people who don't drink enough fluids or who lose too much fluid, those who eat a high-protein diet, and those who have gout. Certain genetic factors also may increase your risk of uric acid stones.
Cystine stones. These stones form in people with a hereditary disorder that causes the kidneys to excrete too much of certain amino acids (cystinuria).
Risk factors
Factors that increase your risk of developing kidney stones include:
Family or personal history. If someone in your family has kidney stones, you're more likely to develop stones, too. And if you've already had one or more kidney stones, you're at increased risk of developing another.
Dehydration. Not drinking enough water each day can increase your risk of kidney stones. People who live in warm climates and those who sweat a lot may be at higher risk than others.
Certain diets. Eating a diet that's high in protein, sodium (salt) and sugar may increase your risk of some types of kidney stones. This is especially true with a high-sodium diet. Too much salt in your diet increases the amount of calcium your kidneys must filter and significantly increases your risk of kidney stones.
Being obese. High body mass index (BMI), large waist size and weight gain have been linked to an increased risk of kidney stones.
Digestive diseases and surgery. Gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic diarrhea can cause changes in the digestive process that affect your absorption of calcium and water, increasing the levels of stone-forming substances in your urine.
Other medical conditions. Diseases and conditions that may increase your risk of kidney stones include renal tubular acidosis, cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism, certain medications and some urinary tract infections.
Diuretics are substances that allow the body to get rid of excess water and sodium. They help in draining out the water by stimulating the kidneys and eliminate sodium from the urine thus, facilitating drainage of excess water. Diuretics are prescribed by the doctor when the body starts to retain excessive fluids.
The conditions that lead to problems such as:
1. High blood pressure: This is a disorder wherein the blood exerts more than the normal force (pressure) against the arterial walls while flowing through them.
2. Diabetes: It is a metabolic disorder wherein the blood sugar level rises significantly.
3. Kidney stones: Kidney stones refer to the formation of stones in the kidneys that can hamper the normal functioning of the kidney, leading to fluid retention in the body.
4. Edema: A disorder wherein parts of the body tend to swell due to inflammation is called ‘edema’.
5. Impaired functioning of the kidney: Impaired functioning of the kidneys makes it very difficult to flush out the excess sodium from the body thus, leading to fluid retention.
There are certain natural diuretics, which can come to your aid in times such as these. Read on to know more:
1. Parsley: Parsley, a very effective diuretic, is an herb that is commonly used for garnishing. It can also help in relieving bladder problems.
2. Black and green tea: Both green and black variants of the humble tea are very effective diuretics; you can enjoy them after a heavy meal to get rid of the bloating.
3. Hawthorn: A type of natural diuretic that is effective in reducing fluid accumulation and increasing urinary excretion. It also helps in treating problems of the kidney.
4. Juniper: A diuretic that has been used since ancient times. Juniper is very effective in removing excess salt and fluids from the body. The advantage of this plant is that it does not lower downs the level of potassium in the body, a side effect of other diuretics.
- Increase your fluid intake: Make sure you drink minimum 6-8 glasses of water every day. You can also consume caffeine-free drinks and non-alcoholic beverages, but if you have a tendency of forming kidney stones then avoid consuming decaffeinated tea. You can also consume watermelon as it contains the highest concentration of water when compared to other fruits.
- Less intake of vitamin C: An amount of VitaminC more than 3000 mgs per day can be a potent reason for the formation of kidney stones. Our body converts vitaminC into oxalate, which in turn leads in the build up of stones. But remember it is also an essential vitamin for the body. So, don't cut down on it completely.
- Increase the intake of vitamin A: It is beneficial for the urinary tract and reduces the formation of kidney stones. Food rich in vitamin A are carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, winter squash & broccoli. An excess of vitaminA can also be toxic as your body will not be able to excrete it; so, do not overeat it.
- Olive oil and lemon juice: Take the same amount of olive oil and lemon juice i.e. 2 oz, mix them and drink straight. Follow it with a glass of water. It will significantly decrease the stone pain and alleviate the formation of kidney stones.
- Some more juice
> Consume 1cup of juice prepared with radish leaves, twice a day.
> Take 3 slightly raw ladyfingers, cut them into thin long pieces and soak them overnight in 2ltrs of water. In the morning, take out the ladyfingers from the water and squeeze their juice into the same water. Drink the entire water after 1-2hrs.
- Consume less meat and fish: People with uric-acid stones, generally, have a diet rich in animal protein. This protein eventually builds up stones. Cut back on food high on protein such as fish roe, herring, mackerel, mussels, sardines and shrimp, wine, red meat and sweetbread.
जेव्हा आपल्याला खूप वेदना होतात तेव्हा आपले मूत्रपिंड दगडांचे प्रथम निदान बरेचदा होते. उपचारांचा सल्ला देण्यापूर्वी आपला डॉक्टर काही प्रश्न विचारेल आणि तुमची तपासणी करेल.
आपण एक दगड पास केल्यानंतर, भविष्यात आपल्याला अधिक दगड असण्याची शक्यता असल्याचे शोधण्यासाठी आपले डॉक्टर आपल्याला दुसरी परीक्षा देऊ शकतात.
आपल्या प्रारंभिक आणि फॉलो-अप परीक्षेत खालील पैकी काही किंवा काही प्रश्न विचारले जाऊ शकतात.
जीवनशैली प्रश्न
आपण किती द्रव पिणे करता? तू भरपूर पाणी पितोस मूत्रपिंड दगडांचे सर्वात सामान्य कारण पुरेसे पाणी पिणे नाही.
तू द्राक्षांचा रस रस पितोस का? द्राक्षाच्या फळाचा रस पिण्यासाठी मूत्रपिंडांच्या धोक्यांमुळे तुमचा धोका वाढू शकतो.
आपण किती सक्रिय आहात? आपल्याला व्यायाम किंवा खेळ खेळायला आवडते का? आपल्याकडे एखादे काम आहे जेथे आपण सक्रिय आहात किंवा आपण कुठे बसलात? शारीरिकरित्या सक्रिय नसलेले लोक किडनी दगड विकसित करतात. आपण व्यायाम आणि घाम घेत असाल तर गमावलेला द्रव पुनर्स्थित करण्यासाठी द्रवपदार्थ न पिणे, आपल्याला दगड विकसित करण्याची अधिक शक्यता असू शकते.
आपण कोणत्या प्रकारचे खाद्यपदार्थ खात आहात? आहारामुळे आपल्याला दगड विकसित करण्याची अधिक शक्यता असते:
गडद हिरव्या भाज्या, चॉकलेट आणि बीन्ससारख्या आहारामध्ये जास्त प्रमाणात खाद्य.
व्हिटॅमिन सी किंवा डी किंवा या जीवनसत्त्वेंचे पूरक असलेले अनेक पदार्थ खाणे.
ज्या पदार्थांमध्ये भरपूर प्रमाणात मीठा (सोडियम) असते.
अन्न किंवा पेय जे कमी कॅल्शियम असतात.
पशु प्रथिने (जसे की गोमांस) जास्त अन्न.
औषध आणि वैद्यकीय परिस्थिती
आपण कोणती औषधे घेत आहात? काही औषधे आपणास मूत्रपिंडांचे दगड वाढविण्याची अधिक शक्यता देतात.
भूतकाळात आपण कोणत्या वैद्यकीय परिस्थितीत आहात किंवा आपल्याकडे आता आहे? वैद्यकीय परिस्थितीमुळे ते जास्त वाढू शकते आपण मूत्रपिंडातील दगडांचा विकास कराल:
गाउट
वारंवार मूत्रमार्गात रक्त संक्रमण (यूटीआय).
मूत्रपिंड प्रणाली असामान्यता इतिहास.
मूत्रपिंड दगड, गाउट किंवा पॅराथ्रॉइड रोगाचा कौटुंबिक इतिहास.
इन्फ्लॅमेटरी आंत्र रोग.
सर्कॉइडोसिस
मागील ओटीपोटात शस्त्रक्रिया.
बराच काळ विश्रांतीसाठी विश्रांती घ्या.
शारीरिक परीक्षा
शारीरिक तपासणी दरम्यान, आपले लक्षणे आपल्या लक्षणेंच्या कारणांचे स्पष्टीकरण देणारी इतर सुचनांसाठी आपल्या शरीराची तपासणी करतील.
आपले तापमान घ्या.
आपले वजन तपासा.
वेदना किंवा द्रवपदार्थ तपासणीसाठी तपासण्यासाठी आपल्या पोटावर (ओटीपोटाच्या पलंगावर) किंवा मागे दाबा किंवा टॅप करा.
वाढलेल्या लिम्फ नोड्सची तपासणी करण्यासाठी आपल्या मानेचे परीक्षण करा.
आपल्याकडे सध्या मूत्रपिंडाचे दगड असल्यास आणि पुन्हा एकदा आपल्याकडे येण्याची शक्यता असल्यास डॉक्टरांचा संपूर्ण चिकित्सकीय इतिहास आणि शारीरिक तपासणी आपल्या डॉक्टरांना मदत करेल.
परिणाम
जीवनशैली आणि वैद्यकीय प्रश्नांचे आपले उत्तर आपल्यास सध्या मूत्रपिंडाचे दगड असल्यास आणि आपल्यास पुन्हा एकदा आढळण्याची शक्यता असल्यास डॉक्टरांना शोधण्यात मदत करेल.
आपल्यास मूत्रपिंडातील दगड असल्याचे दर्शविणारे शारीरिक लक्षणे यात समाविष्ट आहेत:
बाजू, ओटीपोट, गळस किंवा जननेंद्रियामध्ये तीव्र वेदना.
वारंवार आणि वेदनादायक पेशी. मूत्रमार्गात ट्रॅक्ट संक्रमण देखील असू शकते.
कशाबद्दल विचार करायला पाहिजे
आपल्या वैद्यकीय इतिहासावर आणि शारीरिक परीक्षणावर आधारित आपल्या डॉक्टरांनी मूत्रपिंड दगड असल्याचा निर्णय घेतला तरीही ते मूत्रमार्गात किंवा मूत्र संस्कृतीसारख्या लॅब चाचण्या देखील करू शकतात. या चाचण्या पूर्ण होण्याआधी आपले डॉक्टर उपचार सुरू करू शकतात किंवा आपल्याला परिणाम माहित आहेत.
जर तुमच्याकडे मूत्रपिंड दगडांचा कौटुंबिक इतिहास असेल किंवा एकापेक्षा जास्त दगड असेल तर आपला डॉक्टर दगड शोधण्याचा अधिक प्रयत्न करू शकेल.