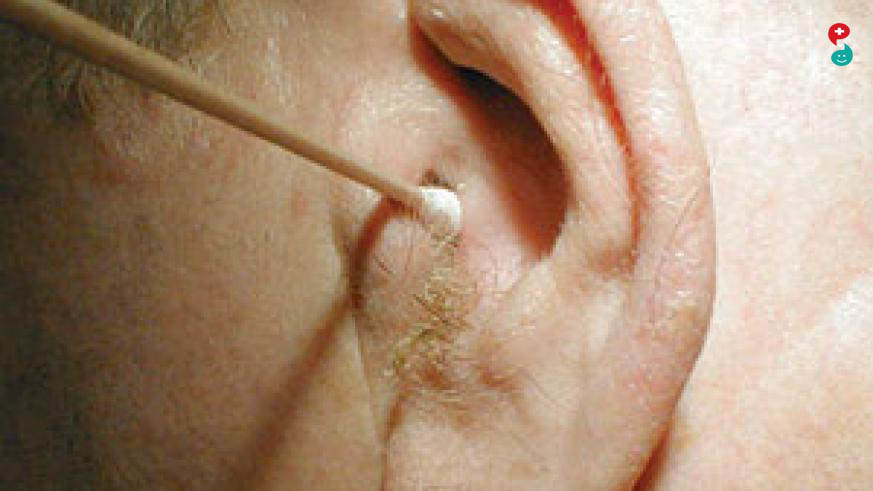
Otitis media is inflammation located in the middle ear. Otitis media can occur as a result of a cold, sore throat, or respiratory infection.
Facts about otitis media
More than 80 percent of children have at least one episode of otitis media by the time they are 3 years of age.
Otitis media can also affect adults, although it is primarily a condition that occurs in children.
Who is at risk for getting ear infections?
While any child may develop an ear infection, the following are some of the factors that may increase your child's risk of developing ear infections:
Being around someone who smokes
Family history of ear infections
A poor immune system
Spends time in a daycare setting
Absence of breastfeeding
Having a cold
Bottle-fed while laying on his or her back
What causes otitis media?
Middle ear infections are usually a result of a malfunction of the eustachian tube, a canal that links the middle ear with the throat area. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear. When this tube is not working properly, it prevents normal drainage of fluid from the middle ear, causing a build up of fluid behind the eardrum. When this fluid cannot drain, it allows for the growth of bacteria and viruses in the ear that can lead to acute otitis media. The following are some of the reasons that the eustachian tube may not work properly:
A cold or allergy which can lead to swelling and congestion of the lining of the nose, throat, and eustachian tube (this swelling prevents the normal flow of fluids)
A malformation of the eustachian tube
What are the different types of otitis media?
Different types of otitis media include the following:
Acute otitis media (AOM). The middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear, causing the child to have a fever, ear pain, and hearing loss.
Otitis media with effusion (OME.) Fluid (effusion) and mucus continue to accumulate in the middle ear after an initial infection subsides. The child may experience a feeling of fullness in the ear and hearing loss.
Chronic otitis media with effusion (COME). Fluid remains in the middle ear for a prolonged period or returns again and again, even though there is no infection. May result in difficulty fighting new infection and hearing loss.
What are the symptoms of otitis media?
The following are the most common symptoms of otitis media. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
Unusual irritability
Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep
Tugging or pulling at one or both ears
Fever
Fluid draining from ear(s)
Loss of balance
Hearing difficulties
Ear pain
The symptoms of otitis media may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your child's physician for a diagnosis.
How is otitis media diagnosed?
In addition to a complete medical history and physical examination, your child's physician will inspect the outer ear(s) and eardrum(s) using an otoscope. The otoscope is a lighted instrument that allows the physician to see inside the ear. A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to test eardrum movement.
Tympanometry, is a test that can be performed in most physicians' offices to help determine how the middle ear is functioning. It does not tell if the child is hearing or not, but helps to detect any changes in pressure in the middle ear. This is a difficult test to perform in younger children because the child needs to remain still and not cry, talk, or move.
A hearing test may be performed for children who have frequent ear infections.
Meniere's disease is an inner ear disease that typically affects one ear. This disease can cause pressure or pain in the ear, severe cases of dizziness or vertigo, hearing loss and a ringing or roaring noise, also known as tinnitus. Although Meniere's disease can affect people of any age, people in their 40s and 50s are much more likely to experience it. This condition is considered to be chronic and there is no cure, but there are various treatment strategies that will minimize the effect on your life and relieve symptoms.
People with Meniere's will have sudden dizzy spells after experiencing tinnitus or muffled hearing. Symptoms vary from person to person, and some will experience many attacks over a period of several days, and others will have an isolated attack every once in awhile.
Potential causes or triggers
Although there is no exact cause of Meniere's, scientists believe that it has something to do with high pressure of the fluid in part of the inner ear. Passages and cavities connect throughout the inner ear, also called a labyrinth. The outside of the inner ear is a bone structure, while the interior is a soft membrane. This part of the ear contains tiny sensors that resemble hairs and respond to the movement of fluid, or endolymph, through the area. Potential causes or triggers of Meniere's disease include:
Head injury
Infection to the inner or middle ear
Allergies
Alcohol use
Stress
Side effects of certain medications
Smoking
Stress or anxiety
Fatigue
Family history of the disease
Respiratory infection
Recent viral illness
Abnormal immune response
Migraines
Symptoms
Meniere's disease varies dramatically from person to person, so individuals can experience an array of different symptoms that occur daily or just once a year.
Classic symptoms: pressure in the ear, hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus
Symptoms usually begin with the feeling of pressure in the ear, followed by tinnitus, hearing loss and vertigo. These episodes will last anywhere from 20 minutes to four hours. People with Meniere's will generally experience episodes in clusters with long periods of remission. When you experience an episode of Meniere's disease, it is best to lie down and focus on one sole, non-moving object. Often times, a sufferer will feel better after taking a nap.
Stages of Meniere's disease and diagnosis
Meniere's disease commonly affects people in various stages, with symptoms developing over time.
Early state: During this time, a person will experience sudden and often out-of-the-blue episodes of vertigo that last anywhere from 20 minutes to an entire day. An individual's ear may feel blocked or full, and they may have some hearing loss, which typically goes away after the episode fades. It is also common to feel the effects of tinnitus.
Middle stage: Symptoms of vertigo tend to become less severe during this stage, while hearing loss and tinnitus will increase in severity. Many people will also experience long-term remission that can last several months.
Late stage: During the late stages of Meniere's disease, patients will not suffer from vertigo as often, and some people will be relieved from it forever. However, tinnitus and hearing loss will likely get progressively worse, and people will likely experience unsteady balance regularly. Most people feel unstable in dark conditions when bearings are off.
Along with the common symptoms of Meniere's disease, it's possible to suffer from depression or anxiety. Since the ailment affects hearing, you may lose the confidence to have conversations with others or at work, which can contribute to depression or anxiety. In addition, symptoms tend to pop up out of nowhere, so those living with Meniere's can live in a constant anxious state unsure of when an episode will occur.
In order to diagnose the disease, you must experience tinnitus, hearing loss and vertigo more than once. Since all of these issues can stand alone or be associated with other diseases, Meniere's can sometimes be difficult to diagnose.
Treatment options
Since Meniere's disease is not curable, many treatment options involve patients changing their habits or diet, or taking medications. Dietary changes can decrease the amount of fluid in the inner ear, which can weaken the symptoms of the disease. These changes include:
Salt intake: Salt helps the body to retain water, so reduce intake of sodium-rich beverages and foods.
Decrease caffeine: Caffeinated beverages can make symptoms like tinnitus worse, so it is best to decrease the amount of this stimulant in your diet.
Monosodium glutamate (MSG): Although many food manufacturers have begun to woman's hand holding salt shaker
Decreasing sodium in your diet can help
symptoms of Meniere's disease.
avoid using MSG because of its harmful properties, it is still important to check labels to make sure it is not added.
Smaller meals: More experts are proving there are greater benefits to the body if you consume five to six smaller meals throughout the day instead of three larger meals. This dietary pattern can also improve symptoms of Meniere's disease by keeping the metabolism moving and bodily fluids regulated. Similarly, opting for a healthier lifestyle can decrease the amount and severity of Meniere's disease symptoms.
Smoking: Many people who suffer from Meniere's disease and who regularly smoke report weakened symptoms after quitting.
Stress management: Stress and anxiety are both linked to Meniere's disease, but both can be a cause and symptom of the disease. Learning how to manage and identify stressors can bring relief. It may be beneficial to try relaxation or meditation techniques.
कानाचा संसर्ग म्हणजे काय?
कानांच्या संसर्गास मध्यवर्ती कान संसर्ग म्हणतात, हे मुलांमध्ये सर्वात सामान्य परिस्थिती आहे. ते दुर्लक्ष केले जाऊ नये. अनियंत्रित कान संक्रमण आपल्या मुलासाठी अनावश्यक वेदना आणि कायमस्वरुपी बहिरेपण होऊ शकते. कानाचा संसर्ग जीवाणू किंवा व्हायरल संसर्गामुळे होते. इस्टॅचियन ट्यूब नावाच्या आतील बाजूस आणि गळ्यात मागे असलेल्या लहान जागेत दबाव निर्माण होतो. लहान इस्टॅचियन नलिका दबाव अधिक संवेदनशील आहेत, ज्यामुळे कान दुखणे होऊ शकते. मुलाच्या ऍडेनोइड्स (गळ्याच्या मागील बाजूने टॉन्सिल्सच्या वर असलेल्या टिशूचे छोटे तुकडे) इस्टॅचियन नलिका उघडण्यास अवरोधित करतात कारण ते लहान मुलांमध्ये मोठे असतात.
एलर्जी, सर्दी, बॅक्टेरिया किंवा व्हायरसपासून नाक किंवा श्लेष्मातून ड्रेनेज भरल्यावर यूस्टॅचियन नलिका योग्यरित्या कार्य करत नाहीत कारण ड्रेनेज ज्यामुळे वेदना होतात. तीव्र कानाचा संसर्ग 6 आठवडे किंवा त्यापेक्षा जास्त काळ टिकू शकतो, परंतु बहुतेक दिवस 3 दिवसांनी स्वत: जातात. काही कान वेदना बाळंतपणात वाढतात, इअरवॅक्सची उभारणी किंवा आपल्या मुलांनी त्यांच्या कानांमध्ये ठेवलेली परकीय वस्तू. जेव्हा दबाव वाढतो, तेव्हा आपल्या मुलाच्या अंगठ्याला तोडणे किंवा पॉप करणे, होऊ शकते. प्रारंभिक पॉप दुखतो परंतु प्रत्यक्षात दबाव आणि वेदना कमी करतो.
लक्षणे
कान संक्रमण लक्षणे
आपल्या मुलाच्या प्रभावित कानात तीव्र वेदना सहसा कानाच्या संसर्गाचे पहिले लक्षण असते. लहान मुले आपल्याला सांगतात की त्यांचे कान दुखते, पण बाळ केवळ रडतात. वेदना रात्रीच्या वेळी आणि जेव्हा आपला मुलगा च्यूइंग, किंवा झोपायला लागतो कारण त्या वेळी दाब सर्वात मोठा असतो. इतर लक्षणांमध्ये खोकला, ताप, उलट्या, किंवा चक्कर येणे आणि कमी ऐकू येणे यांचा समावेश होतो.
सतत, वारंवार कान संक्रमण कमी ऐकू येण्याचे कारण होऊ शकते.
कारणे
कान संक्रमण का होतो?
कान संक्रमण विषाणूजन्य संसर्गामुळे होतात. संक्रमण गळ्यात मागे असलेल्या लहान जागेत दाब निर्माण करतो. या क्षेत्राला युस्टाचियन ट्यूब म्हणतात. एलर्जी, सर्दी, जीवाणू किंवा व्हायरसमधून नाक किंवा श्लेष्मातून ड्रेनेज भरल्यास या नळ्या योग्यरित्या कार्य करत नाहीत.
प्रतिबंध
कान संक्रमण टाळले जाऊ शकते?
कान दुखणे संक्रामक नसले तरी, जीवाणू किंवा विषाणू ज्याला कारणीभूत ठरते ते बर्याचदा बहुतेक रोगांसारखे महत्वाचे आहे:
- अनेक प्रकारच्या न्यूमोकोकल बॅक्टेरियापासून बचाव करण्यासाठी आपल्या मुलास न्यूमोकोकल कन्जगेट लस द्या. या प्रकारचे जीवाणू कान संक्रमणांचे सर्वात सामान्य कारण आहे. वेळेवर आपल्या मुलाची लसीकरण करा.
- नियमितपणे हात धुणे आणि अन्न आणि पेय सामायिक करणे टाळा
- धुम्रपान टाळा.
- पहिल्या 6 महिन्यांपर्यंत आपल्या बाळाला स्तनपान करा आणि किमान 1 वर्षासाठी स्तनपान चालू ठेवा.
- सामान्य एलर्जी आणि शीत औषधे कानांच्या संसर्गापासून संरक्षण देत नाहीत.